In the ever-evolving landscape of architecture, innovation is the key driving force shaping the future of design and planning. One such groundbreaking innovation that has significantly transformed the industry is the advancement in printing technology. From 3D printing to large-format printers, these technologies have not only revolutionized the way architects conceptualize and create designs but have also enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness in architectural practices.
Introduction
Let us dive into the world of BIM to wield its power to the maximum potential. This is your roadmap to explore essential insights to equip you for success in the BIM realm, covering everything from software selection to mastering project management. Before we go ahead, if you are new to the concept, check out our previous blogs – BIM: Your Passport to Make a Mark in the Digital Revolution of AEC! and AEC in Transition: Traditional V/S BIM Professionals to understand why BIM is such a demand! Let’s embark on this exciting journey together!
Understanding BIM Software
The 3 Cs of BIM are its 3 core functionalities:
Creation
Coordination, and
Circulation
BIM is more than software—BIM revolutionises workflow, collaboration, data interaction, and system reinvention.
Getting Started with BIM Software
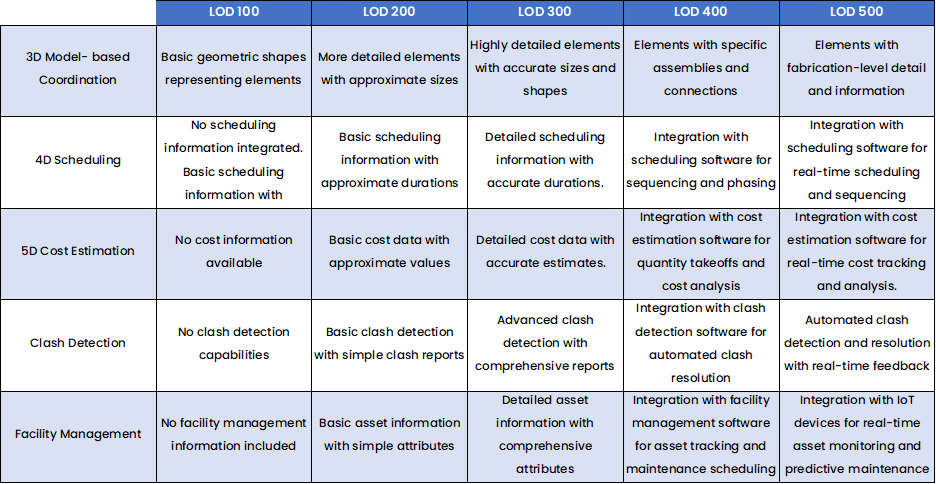
Basic understanding of LODs
Getting Started with BIM Dimensions
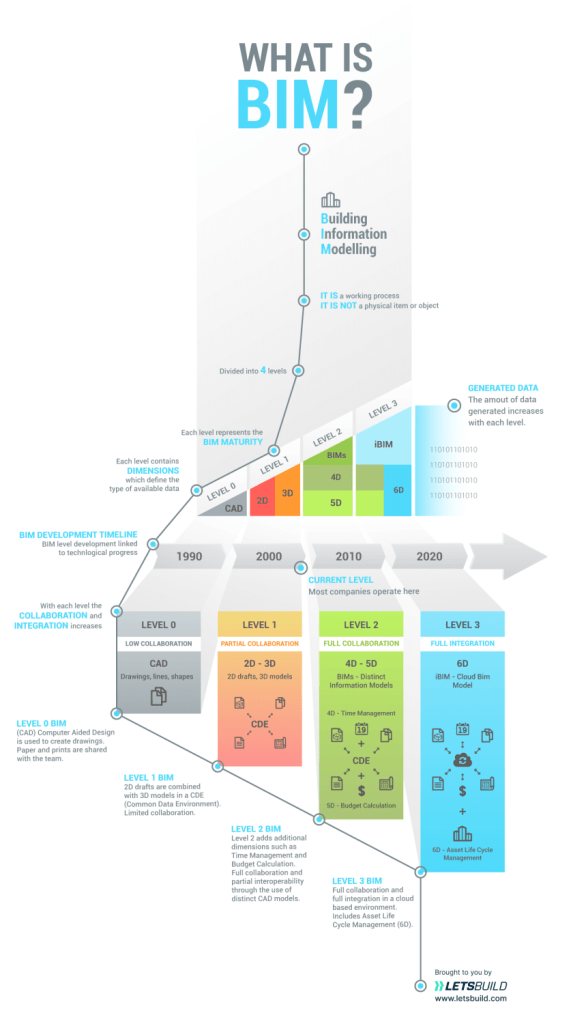
Choosing BIM Software might feel overwhelming, but it’s crucial for your AEC needs. Take a moment to understand your requirements and choose from the following maturity levels of BIM:
3D (Digital model) – for project information, consisting of visualization, drawings and data.
4D (Time) – for planning and scheduling construction activities
5D (Cost) – for estimating budget and tracking costs
6D (Operation) – operation and facility maintenance from construction to completion
7D (Sustainability) – estimating and reducing energy consumption
8D (Safety) – drawing emergency plans and preventing safety issues
Older BIM levels lack collaboration, but Level 1 introduces partial collaboration.
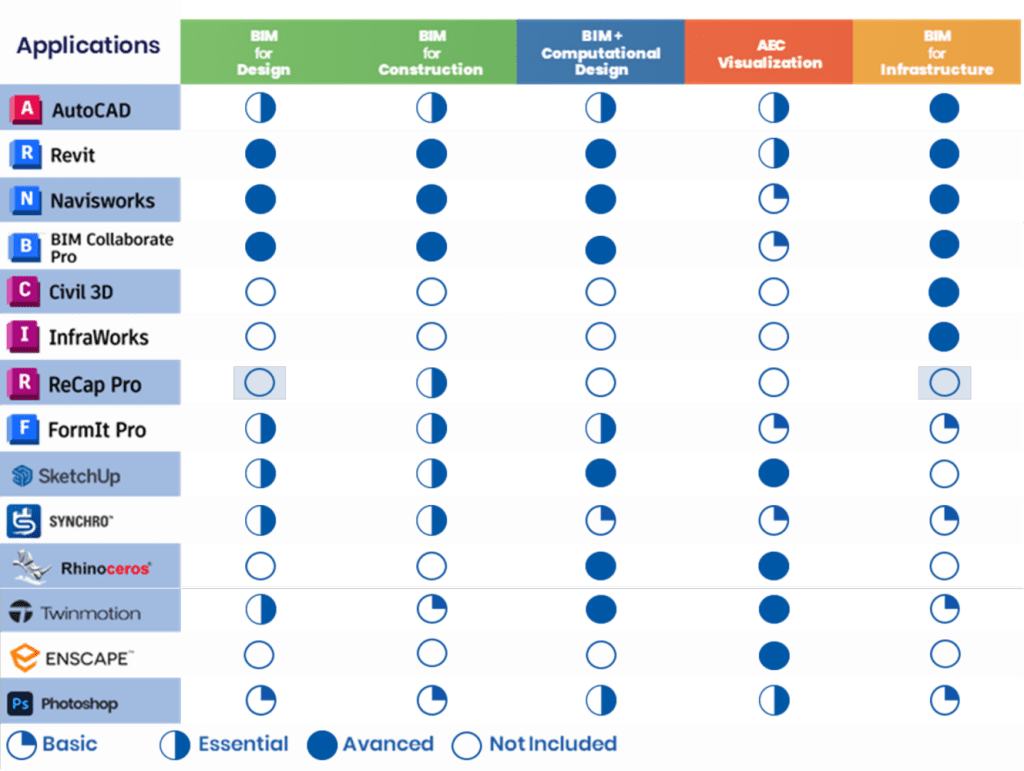
Applications of BIM
The following are different applications you can delve into and the level of understanding required as beginners-
Creating and Managing Projects
- Initiating a new project in BIM-based applications is simple.
- Define project parameters: location, units, project type.
- Use built-in or custom templates.
- Seamlessly import existing project data.
- Collaborate via cloud platforms or built-in tools.
- Organise files for effective version control.
2. Modelling and Designing

- Modelling in BIM software such as Autodesk's Revit, ArchiCAD, and Tekla 3D is at the core of building design.
- Use intuitive tools for architectural, interior designs, landscape, facade, structural, MEP and specialised vertical transportation elements.
- Follow best practices for precision and accuracy.
- Explore advanced techniques like parametric modelling.
- Iterate models based on stakeholder feedback for optimal outcomes.
3. Collaborating and Sharing

- BIM software such as Autodesk’s BIM 360, SketchUp’s Trimble Connect, or Bentley’s ProjectWise fosters seamless collaboration.
- Enable real-time communication and coordination.
- Generate clash detection & clash resolution model.
- Share project data effortlessly in industry-standard formats.
- Embrace cloud-based collaboration for accessibility and flexibility, which enables them to work with teams across the globe.
4. Analysing and Visualizing Data

- Utilise BIM software like Navisworks, Autodesk Construction Cloud (BIM 360), Synchro 4D Pro, and Revizto for different analyses.
- Conduct clash detection for conflict resolution.
- Perform energy analysis to enhance sustainability.
- Estimate costs accurately.
- Leverage data visualisation for effective communication.
5. Construction Documentation
- Organising and creating sheets to represent different drawing sets.
- Managing and tracking revisions to drawings.
- Exporting drawings to different formats (PDF, DWG, etc.).
BIM Śāstra
BIM Śāstra is bimgrafX academy’s training and placement program with a holistic learning approach towards BIM through 3 meticulous levels in various streams.
Level 1
The Beginning – is the software training level encompassing Software Mastery, Guided Self-learning and Finishing School.
BIM Śāstra
Level 2
The Honing – is the Live Project Training level where you will work on a mixed-use building project under the guidance of a personalised mentor.
Level 3
The Becoming – is the final level of a Paid Internship where you will work alongside BIM experts in the industry as well as interact with various stakeholders.




